
What is Refraction of light Leverage Edu
Why can you see your reflection in some objects? In this video we will look at ray diagrams for reflection, refraction and colour absorption. Visible light i.
Lab 10 Reflection and Refraction
(a) Light reaches the upper atmosphere of Earth by traveling through empty space directly from the source (the Sun). (b) This light can reach a person in one of two ways. It can travel through a medium, such as air or glass, and typically travels from one medium to another. It can also reflect from an object, such as a mirror.

draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate the Dispersion of a narrow beam of white light when it
A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. There are a few important things to note: Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium).
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from (i) air KnowledgeBoat
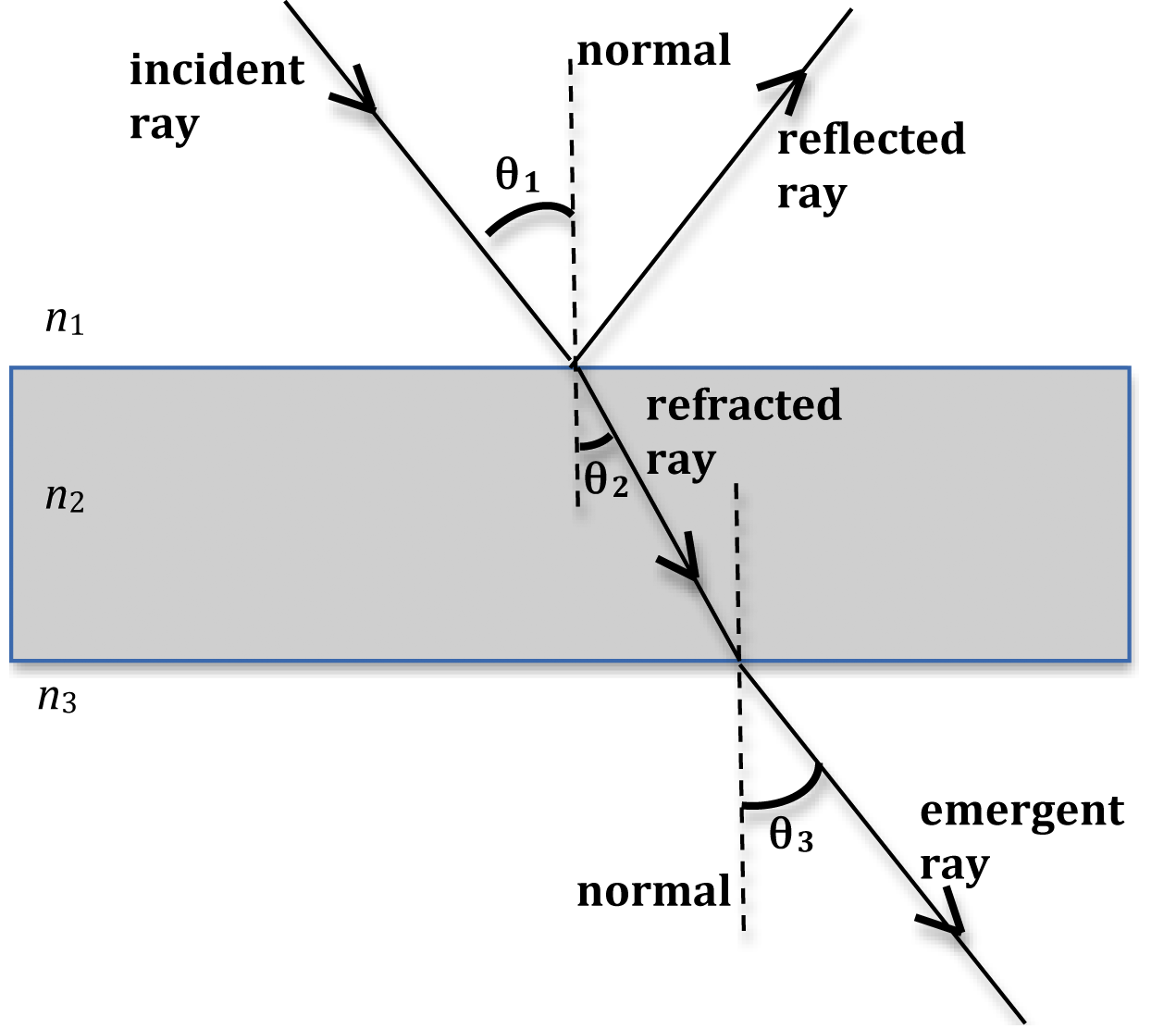
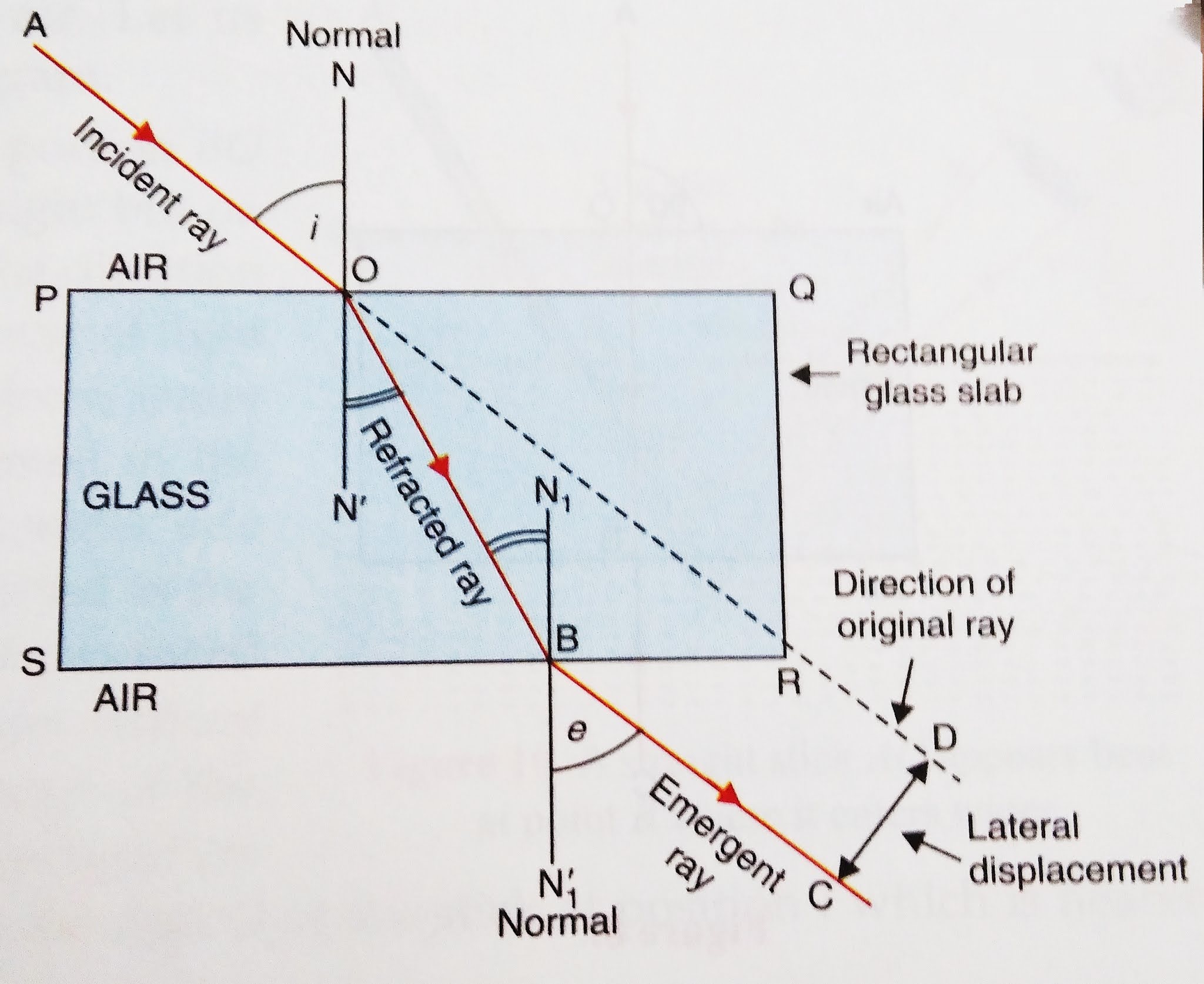
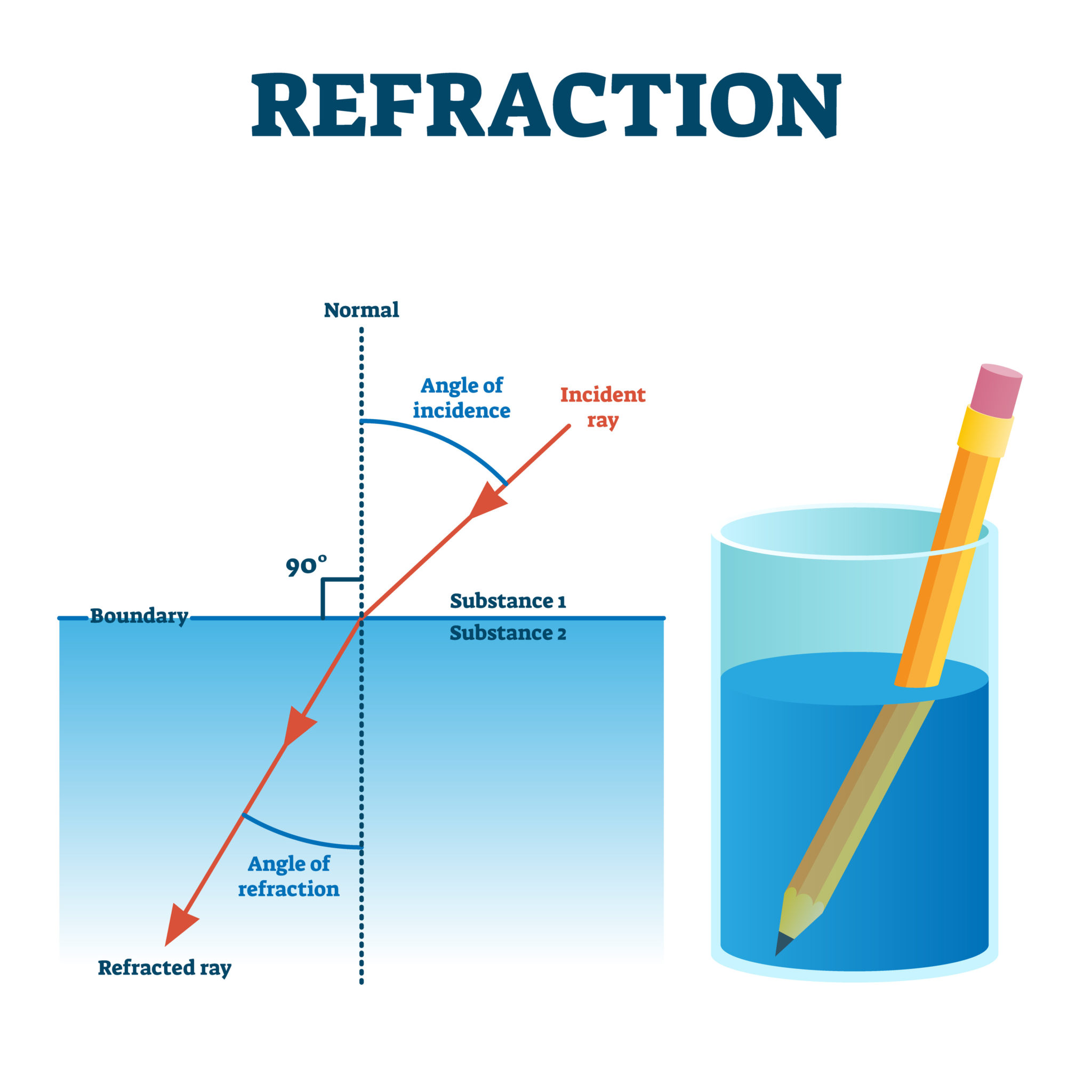
The changing of a light ray's direction (loosely called bending) when it passes a boundary between materials of different composition, or between layers in single material where there are changes in temperature and density, is called refraction.

Ray Diagram Concave and Convex Mirrors Tricks to remember ray diagrams Class 10 Light YouTube
By examining the ray diagram of a spherical mirror, we can gain insights into the fascinating phenomena of reflection and image formation. Table of Contents What is a Mirror? Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirror Characteristics of Concave and Convex Mirrors Concave Mirror Definition Characteristics of Concave Mirrors Convex Mirror Definition
Refraction Ray Diagram Gambaran
How does a lens or mirror form an image? See how light rays are refracted by a lens or reflected by a mirror. Observe how the image changes when you adjust the focal length of the lens, move the object, or move the screen.
PPT CHAPTER17 Light and Image Formation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1365564
The same thing happens to a light ray when it moves from air to water, or from any fast medium to a slow medium: it bends toward the normal.. Light diffraction through glass diagram with overlay. Consider the following. Say you're at the aquarium, and there's a tank that's totally full of water, so there's glass over the top and.
Specular and Diffusion ReflectionHow Light Reflects MooMooMath and Science
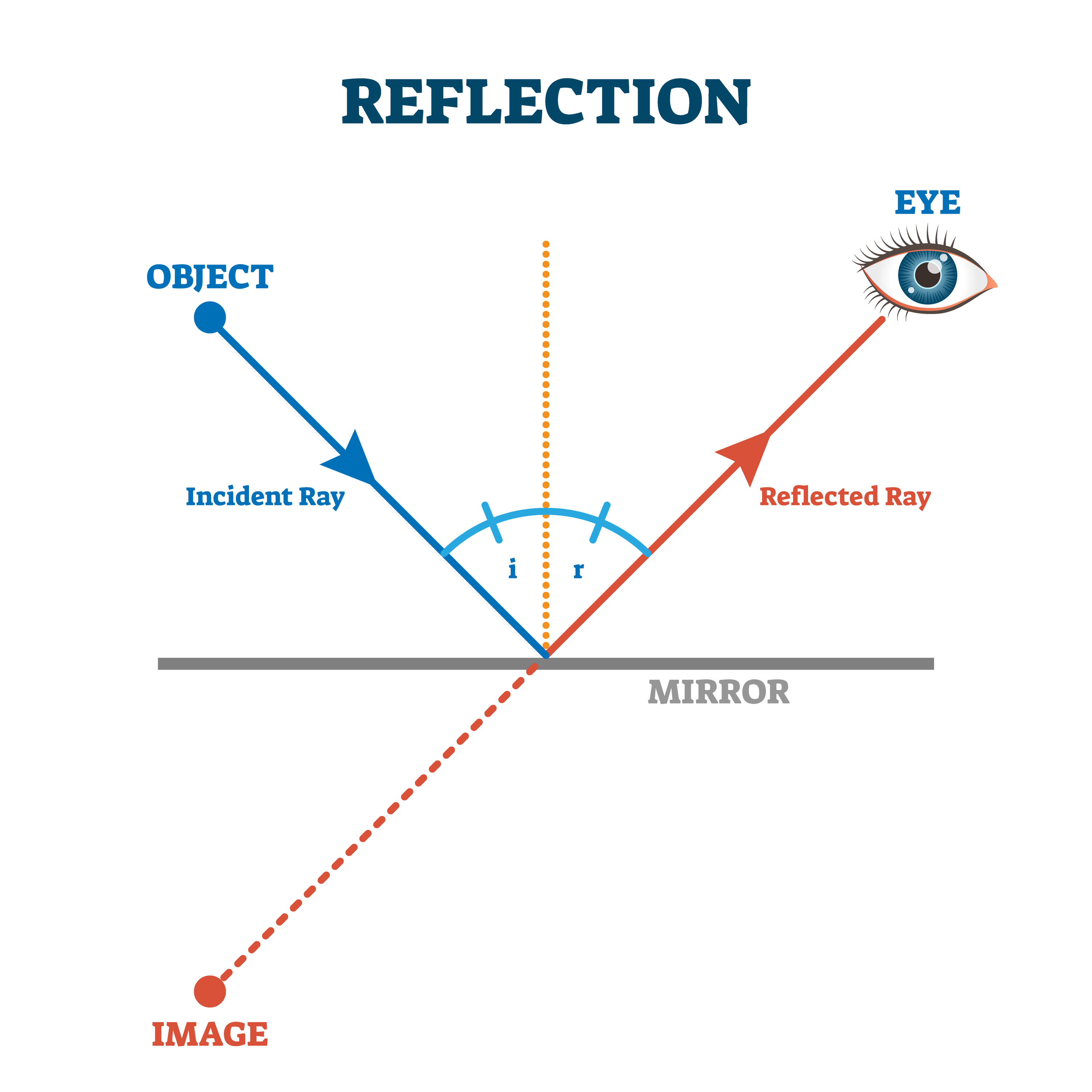
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.

Draw well labelled ray diagram of the reflection of light through plane mirror ? Brainly.in
The Mirror Equation - Convex Mirrors. The ray nature of light is used to explain how light reflects off of planar and curved surfaces to produce both real and virtual images; the nature of the images produced by plane mirrors, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors is thoroughly illustrated.
What is Refraction?
A ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. Complex objects such as people are often represented by stick figures or arrows.

Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
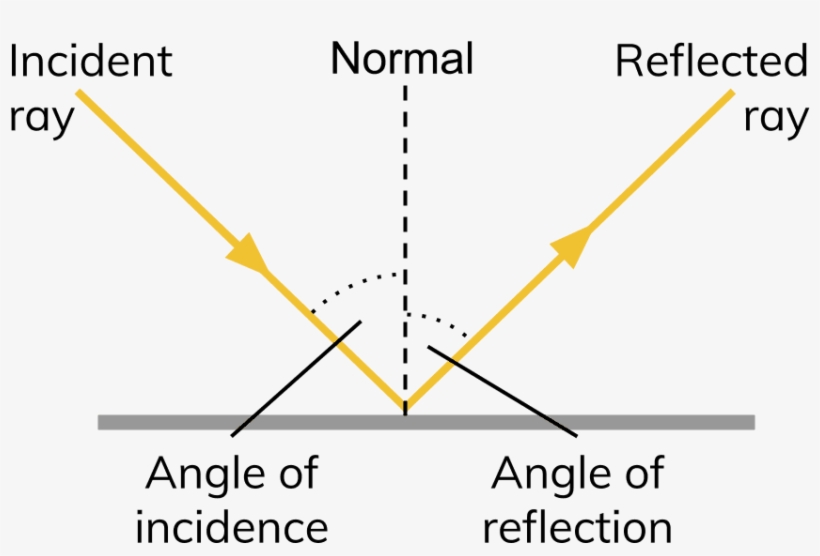
Diagram Of A Light Ray Being Reflected By Diagram Free Transparent PNG Download PNGkey
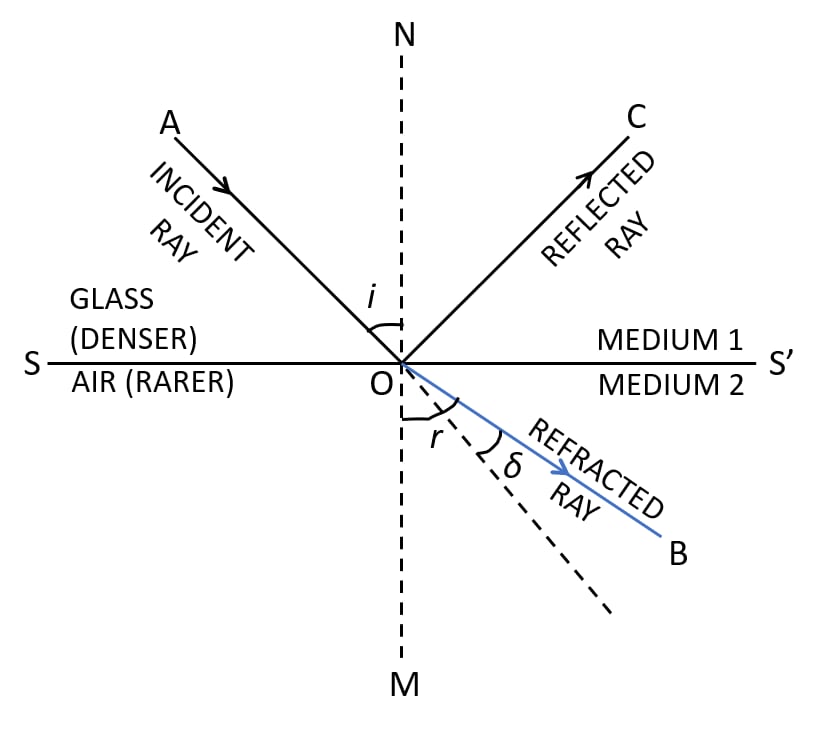
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and (ii) The incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane. These laws of reflection are applicable to all types of reflecting surfaces including spherical surfaces.
PPT Ray Diagrams PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6878954
Ray Diagrams Light is one of the cornerstones of physics. By understanding how light behaves, we have been able to create tools that change the way it travels. Some examples include mirrors and lenses, which we combine to make telescopes for studying distant stars or microscopes to observe life at the microscopic level.
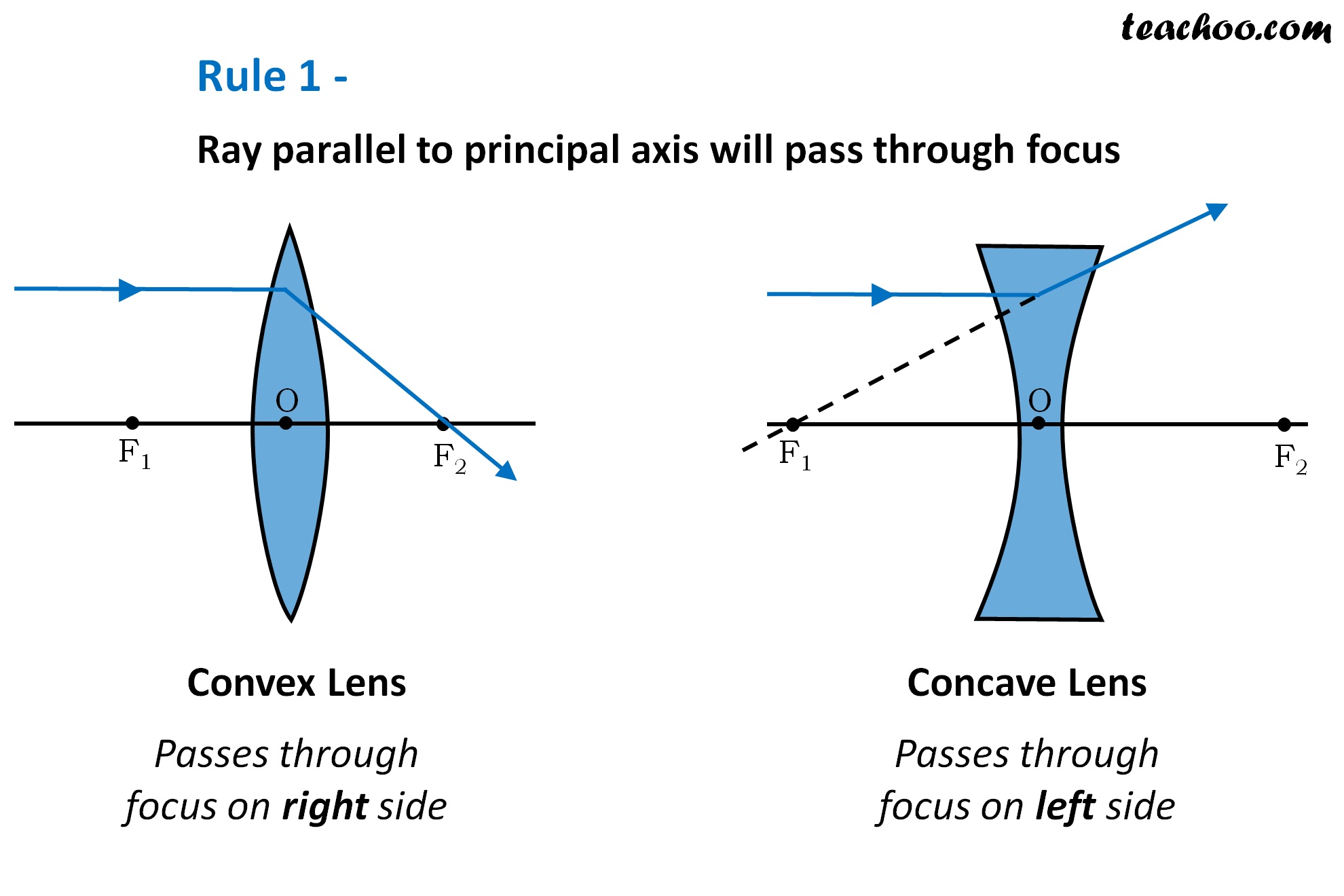
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
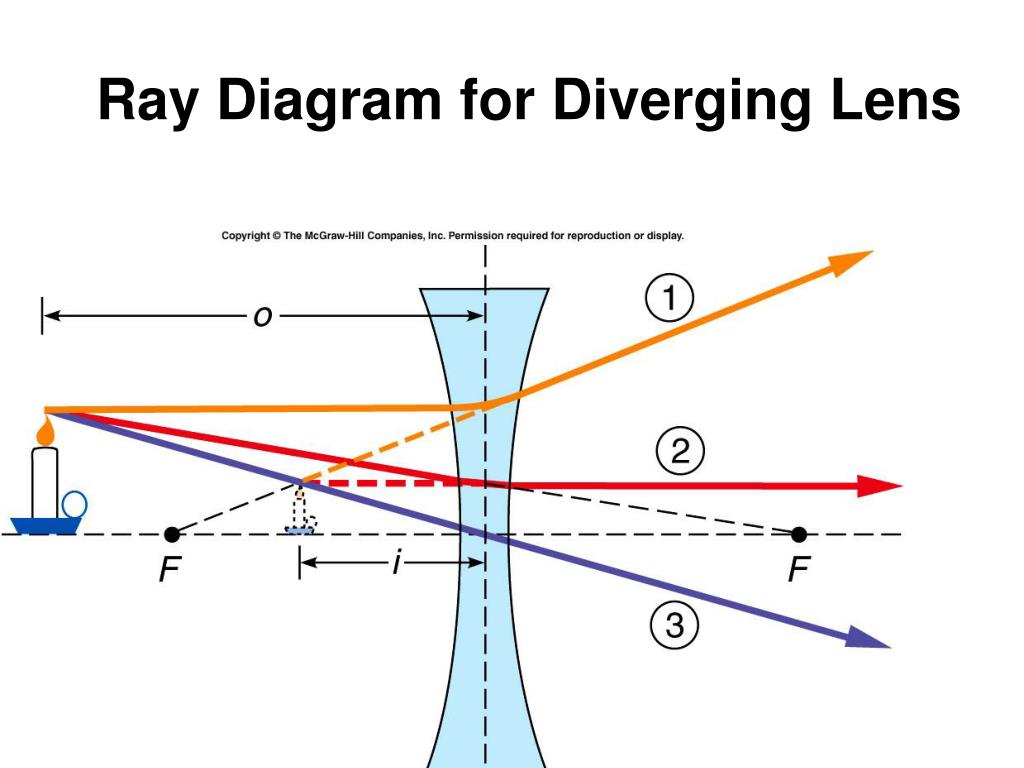
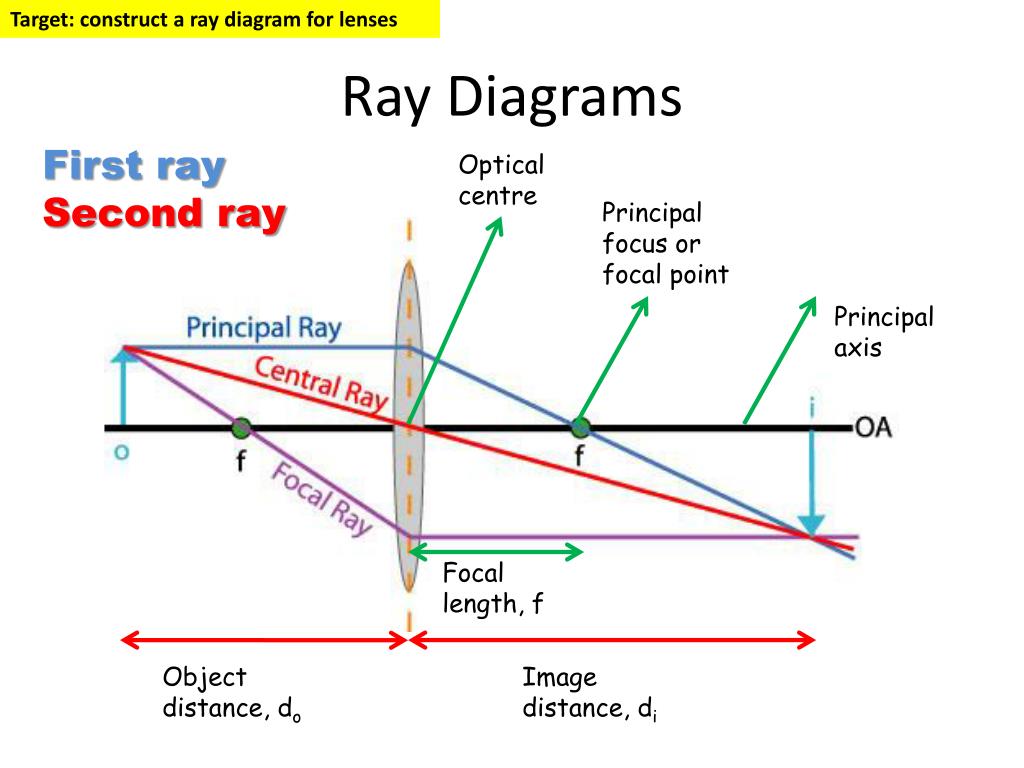
Ray diagrams are a useful tool in understanding the behavior of light as it passes through lenses. Lenses are transparent objects that can bend or refract light, and ray diagrams help visualize how light rays interact with lenses. By tracing the path of light rays, we can determine the location and characteristics of the image formed by a lens.
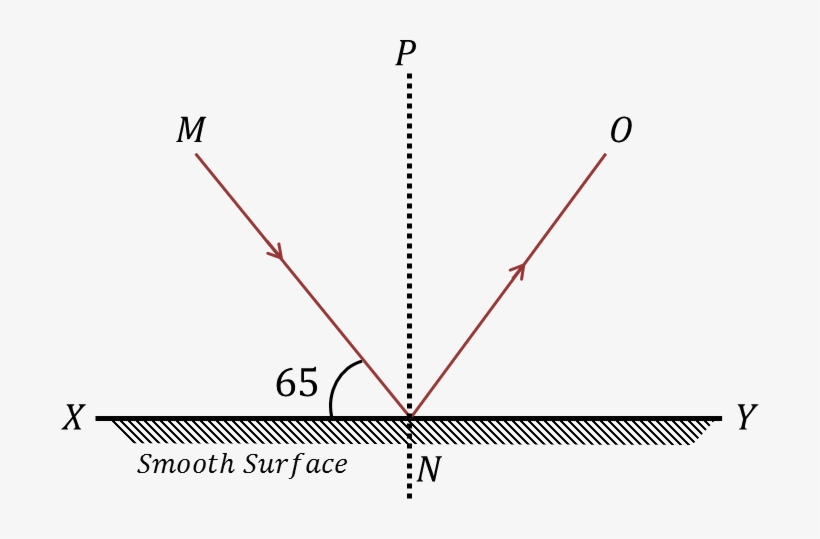
Reflection Of A Light Ray Diagram Free Transparent PNG Download PNGkey
1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis.
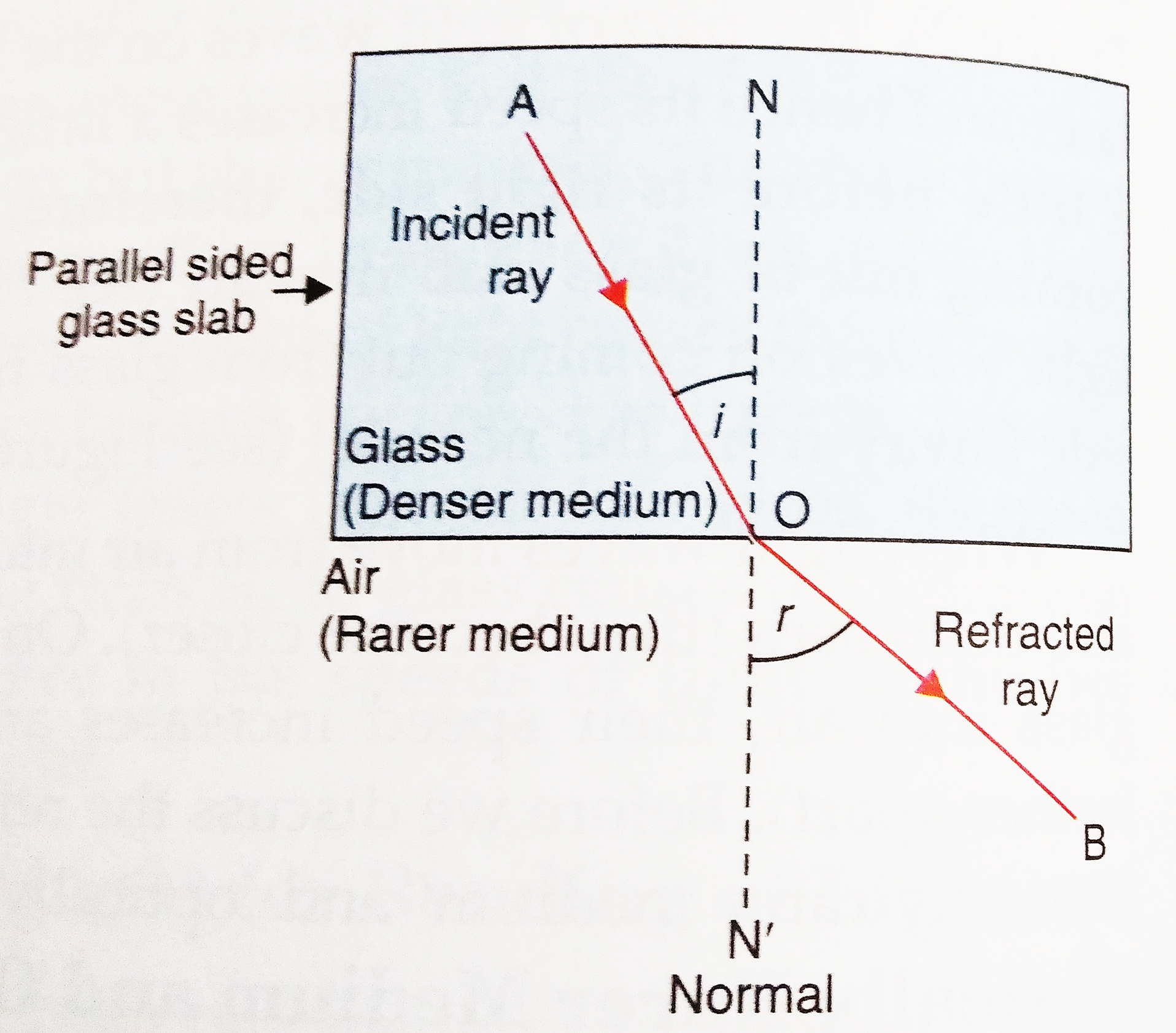
Refraction of Light Refraction, Laws of Refraction, Refractive Index
This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging lens, concave mirrors, and convex.